|
The Ethernet was in minds of technicians for a long time connected
with shared transmission medium in the form of thick and thin coaxial
cable or hub with wide collision domains and above all with
nondeterministic principle of collision solution by CSMA/CD (Carrier
Sense with Multiple Access and Collision Detection). All stations in
collision domain can receive together, but only one can transmit. If
there is a collision, caused by transmitting of more than one station,
all stations turn off for random period of time, before any of them
tries it again. At low network load, this very effective method caused
exponential increase of collisions when increasing the load.
These problems disappeared by the start of using switches.
Nowadays, the collision domain usually contains only two participants
- end device and switch. Cables contain up to four twisted pairs and
transmission runs concurrently witháreceive ináfull duplex
mode. Transmission medium is not shared and it does not make any
collisions. Transmission speed can steadily reach the most possible
level. Such network can be decent basis of communication even for very
complicated and extensive automation systems.
As well as the Ethernet represents the best variant for wide
networks, in case of connecting peripheral units to computers, the
best choice is USB connection. This standard of universal serial bus
originated in 1995 and its quicker variant USB 2.0 withá480
Mbit/sábit rate exists more than ten years too. USB represents
obvious qualitative progress against all formerly used serial and
parallel interfaces. Its reliability, endurance, transmission speed
andáresponse time predetermines it for majority connected
peripheral units inátask of data collection and industrial
automation.
Ethernet nor USB are not new and untried technologies. These
standards did not have an easy way to the branch of industrial
automation. Their dominance is obvious and their qualities
indisputable. Building an Ethernet network is actually extremely easy,
cheap and quick and all system integrators handle this task without
difficulties. Andábuilding a network of peripheries communicating
over USB is even easier.
Serious requirement on communication ináautomation systems is
working ináreal time. Working in real time does not require only
short responses and high speed transmissions, but above all,
deterministicity. It means, the system must guarantee the response in
requisite time - and time response requirements differs case-by-case.
The guaranteed time response is related to stability of time response
as well. The requirements on tolerance of time response significantly
differ in single applications.
According to time requirements and the requirements on
stability of time response of communication network, it is possible
to distinguish approximately three types of industrial Ethernet
network:
Real time is solved through software under standard layers
IP, UDP a TCP. This organization works in all standard networks and
they reach time responses counted in milliseconds with the right
segmentation of the network. This standard architecture is the
cheapest, easiest to realize and satisfy in the majority of
industrial networks. As an example of such solutions is e.g.
Modbus/TCP or DataLab. Real time is solved through software substituting standard
layers IP, UDP a TCP. These networks work with standard network
adapters, communication software works in real time directly under
Ethernet packets and in reserved segments of network reaches
responses andáprecision suitable even for iápro demanding
applications e.g. onáarea of drives and robotics. The highest requirements on real time are solved by
combination of special hardware and software. It is impossible to
use standard network adapters here and these networks usually work
with its own identification of single nodes without necessity of
assigning IP addresses. Communication packets are not usually read,
interpreted and consecutively further posted, but permeate through
by single node witháminimum delay counted in nanoseconds to
another device. Data are given on reserved space in data telegram,
which circle on network. Real time communication packets have the
priority in network before packets of standard network layers IP,
UDP and TCP.
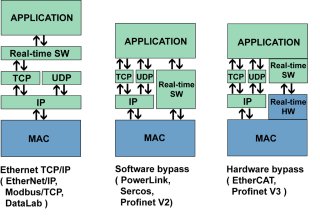
Three principles of solving the communication in real time
in Ethernet networks In different network solutions of industrial Ethernet is
for keeping the demands on punctuality of message delivery able to
use:
star structure witháswitches and not with hub communication models publisherá/ásubscriber and
producerá/áconsumer instead of clientá/áserver
model priority Ethernet packets high-speed variants of Ethernet network segmentation synchronization on principle of distributed real time
hours
Ethernet network is important medium for connecting and integration
of many automation applications into one scope with the option of
central management and supervision. Single applications within the
enterprise can work independently without the necessity to communicate
with other systems in real time and yet can be part of one centrally
managed complex. Stand-alone applications do not have to have their
own displays or any other human - machine interface, they can be
equipped by uninterruptible power supply and can permanently run
irrespective of the state of company computer network.
Applications, which have no displays of their own nor even own
computer, can be run in the environment of the Ethernet network.
Aánumber of stand-alone applications can run on single dedicated
server. The management and maintenance of system becomes even more
simple and it is also possible to spare considerable finance on buying
a upgrading computers and control units. The reliability of network
infrastructure here is substantive, but nowadays it is not usually a
problem.
Connection over Ethernet:
+ practically unlimited distance of connection (dedicated
segment withátwisted pair to circa 100 m) + time response counted in milliseconds - power supply is not always part of communication standard (
standard Power over Ethernet defines options of power supply of
Ethernet devices through data conductors from CAT5 cabling, voltage
of 44 ľ 57Vá is usually used with max. current of 550 mA
) - it is necessary to assign fixed IP address - it is necessary to configure the device through inbuilt
HTTP server before the first use
Connection over USB:
+ time response counted in milliseconds + high transmission speed 480MB / sec, sufficient
transmissive capacity even for high definition digital
cameras + power supply is fixed part of bus + plug-and-play without the necessity of
configuration - the distance of connection to 5m (witháactive
extension to circa 30m)
DataLab IO/ETH units with Ethernet interface are fully compatible
with all I/O modules of DataLab IO system. Only USB interface is
replaced by 10/100 Mbit Full Duplex Ethernet interface and the unit
communicates through TCP/IP protocol. TCP/IP protocol can be easily
routed through various network, the physical distance of the unit from
a computer is practically not limited. From the point of view of
application program equipment, the USB and Ethernet units do not
differ. It suffices in parametrical file of identical driver to choose
the way of communication and set the proper addresses. Then the
applications communicate identically with single units. The
communication with Ethernet units is encrypted and that prevents from
unauthorized interventions in the technology.
The components for industrial automation with the option of
Ethernet and USB connection make integration of applications to
connected centrally managed environment easier and make the building
of modern integrated systems significantly cheaper.
rc
| 